Types of poverty
- Absolute poverty: Daily struggle for survival. People do not have enough resources to pay/cover their basic needs (rent, food, drink, etc.).
- Relative poverty: the importance of social inequality. You have less money than most others and can afford important things or activities.
- Perceived poverty: The feeling of social isolation, a kind of subjective perception of social and material deprivation despite sufficient income.
What percentage of people in Hagen/Germany are affected by poverty?
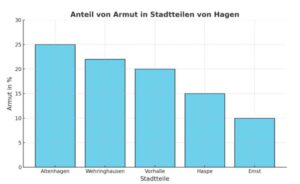
In Hagen, 17.5 % are affected by poverty. In Hagen there is only a general estimate - in certain neighbourhoods such as Altenhagen, Wehringhausen and Vorhalle, for example, the poverty rate is 20-25 %.
What options are there to combat poverty?
Social assistance and citizen's allowance (the citizen's allowance replaces the former basic income support and helps people who are unable to earn a sufficient income, and in particular supports the long-term unemployed, single parents and families in need)
Labour market programmes (through programmes such as "Hartz IV", now "Bürgergeld" and various labour market policy measures, the long-term unemployed are to be integrated into the labour market through training and support)
Housing benefit (offers people on low incomes the chance to still be able to pay rent)
Child benefit and supplementary child allowance (these benefits are intended to relieve the burden on families, especially those living on a low income)
Education and participation (through the education and participation package, children from low-income households receive grants for school materials, tutoring or excursions).
Demands for a minimum wage (the statutory minimum wage, which was raised to €12 per hour in 2024, is intended to ensure that even low earners can earn a living wage)
Causes of poverty:
- Economic factors:
Unemployment, unfair salary distribution - Educational resources:
People without a good education have fewer opportunities to be well paid and thus to ensure long-term financial security. - Political factors
- Social factors:
Discrimination, family structure - Health problems:
Disabilities etc. prevent safe working opportunities.